The wart is a benign neoplasm of the skin that occurs due to the proliferation of cells in the epidermis and papillary dermis, caused by the human papillomavirus, which is transmitted by contact.
Warts: causes, types, diagnosis and treatment
A wart is a predominantly benign localized formation caused by epidermal hyperplasia. Papules and papillomatous growths appear more frequently due to the activity of viral infections. The main reason for its occurrence is the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in the body. HPV infection occurs through home contact, as a result of which the viral flora penetrates the skin or mucous membranes. Various injuries to the skin and mucous membranes, as well as weakened immunity, increase the risk of infection.
As the statistics show, more than 60% of the population has HPV. At the same time, symptomatic HPV may not manifest itself even throughout life. Warts, many of which are called papillomas, appear on the skin and mucous membranes only if there are favorable factors for this.
There are different types of warts, the appearance of which is caused by one or another type of virus. Each type of skin lesion can be located on the skin or mucous membranes. It is not always possible to eliminate the virus from the body.
Warts on the legs, arms and other parts of the body in adults
Men and women are equally susceptible to infection by the human papillomavirus and, consequently, to the appearance of neoplasms, such as warts on the skin and mucous membranes. The penetration of the virus into the body is possible, both with the usual handshake or with the use of general hygiene products, and during sexual intercourse. Once in the human body, the virus enters the scaly epithelium of the skin and actively multiplies it. The HPV incubation period can range from one to a month and a half to six months or more.
Warts on the face, genitals and other parts of the body in women

Warts in women can appear on any part of the body, at any time in life. In shape, color and size, they can be different, ranging from small flat warts on the face of white color, ending in dark genital warts on the mucous membranes of Organs genitals. It is worth mentioning that genital warts, according to research results, can cause the development of cervical cancer. In addition, the official confirmation received the list of warts, which are an external manifestation of HPV, with an increased risk of breast cancer.
Papillomas and warts in men
The strong sex organism is less susceptible to infection and active reproduction of the virus in general and to the appearance of papillomas and warts in particular. Only a marked decrease in immunity caused by various diseases can cause benign formations to appear on the skin and mucous membranes in men. It should be noted that papillomas and warts on the genitals in men can be located in the area of the coronal and frenulum sulcus, sometimes on the head or body of the penis, on the integument at the entrance to the urethra and directly on its mucous membranes, in the perianal region.
What are the types of warts in children?

People of any age are susceptible to the appearance of warts. But warts are more common in children and adolescents. The reason for this could be several papillomatous viruses. Infection of the child's body usually occurs through contact and domestic means. Children are much more likely to communicate closely with other babies in large groups and easily "catch" multiple viruses from each other. In addition, a child can become infected with the mother's papilloma virus during intrauterine development or during childbirth.
Warts: causes of appearance
Many factors can contribute to the appearance of warts. The transmission of the papillomatous virus, as mentioned earlier, occurs through close contact with an infected person or their belongings. In addition, the carrier of the virus, which has no external manifestations, can also act as a source of infection. In addition, self-inoculation or, in other words, self-infection is not excluded. Therefore, warts on the face and neck can appear after shaving and cosmetic peeling. The same applies to papillomas and warts on the legs, chin and armpits. Several skin lesions only increase the risk of contracting HPV. This usually happens in swimming pools, gyms and saunas.
Provocative factors

The virus that causes warts to form is unlikely to penetrate the body of a healthy person with strong immunity. The risk of infection can be increased by:
- Damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
If they are present, contact with an infected person's skin or an object on which there is a virus is likely to result in infection. HPV can remain in the environment for about 2-3 hours. During this period, the likelihood of someone becoming infected with it is quite high. Injuries (wounds, cuts, scrapes), sweating and, consequently, the constant moisture of the skin only increase.
- High humidity and heat.
This provoking factor is more relevant to the appearance of warts on the legs. Uncomfortable parka shoes that cause excessive sweating on the feet, calluses and skin lesions can cause epithelial growths, such as warts on the feet.
- Weakening of the immune system.
Even with the presence of a virus in the body, the appearance of warts is far from being observed. A person can carry the virus for decades and not be aware of it. With strong immunity, the body constantly suppresses the virus, preventing it from multiplying. As soon as the immune system weakens, the virus is immediately activated, which is accompanied by the appearance of external manifestations.
Seborrheic wart
With age, significant changes occur in the human body, which are reflected not only in appearance, but also in health. Thus, a violation of the distribution of the basal cells of the epidermis leads to the appearance of benign formations, called seborrheic warts. On the other hand, these warts are called senile. It is quite simple to identify senile warts by their characteristic appearance:
- they are represented by papules or plaques protruding from the skin surface.
- neoplasms are round or oval;
- they are located, as a rule, on the skin of closed areas of the body, as well as on the face and scalp;
- the color of the warts can be yellowish brown and sometimes even black;
- the size of the formations can vary from 0, 5 to 4 cm.
The limits of seborrheic wart are clear. They protrude slightly above the skin and can be slightly flattened.
If you get these warts on your hands, face, body or head, see a doctor. To determine the most effective and safe tactics for their treatment and removal, it is necessary to perform differential diagnoses, which will distinguish seborrheic warts from:
- Pigmented nevi.
These neoplasms are benign. Like seborrheic warts, pigmented nevi are yellowish-brown or dark, closer to black. Sometimes, the papillomatous surface of the nevi is covered with hair. Its size may be different. In form, neoplasms of this type can be represented by giant plaques or flat papules with a smooth surface.
- Dermatofibromas.
This benign formation is formed from the skin and connective tissues. In their appearance, dermatofibromas have a certain resemblance to blemishes and warts. The surface of the formations can be smooth and keratinized. Its shape is round. Dermatofibroma is partially located in the upper layers of the skin and partially protrudes above its surface. Most of the time, single neoplasms are found. Its color can be different: from gray-pink to purple. Sometimes, dermatofibromas are brown or black. The size of the formations is approximately 1 cm.
- Melanomas.
Unlike dermatofibroma and pigmented nevus, melanomas are malignant tumors. They appear at the spot of stains or at nearby tissue sites. The factors that cause the malignancy of the skin cells are ultraviolet rays, various damages.
Human papillomavirus infection
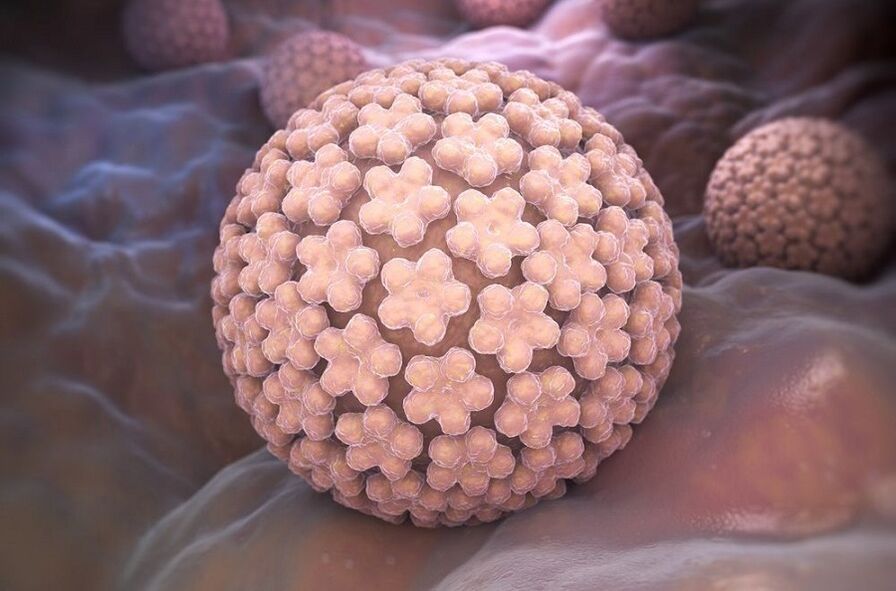
As mentioned earlier, HPV is the cause of HPV infection. So far, more than a hundred of its varieties are known, which can affect the body in one way or another. Each type of virus causes certain types of warts:
- HPV 1 - benign formations on the palms and soles;
- HPV 2 - common (common);
- HPV 3, 10, 28 and 29 - flat neoplasms;
- HPV 4 - warts on the soles of the feet and common warts;
- HPV 6, 11 - laryngeal papillomatosis and genital warts;
- HPV 5, 8, 9, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-25, 36, 39, 40 - generalized manifestation of the virus, which is verrucous epidermodysplasia;
- HPV 7 - common warts;
- HPV 13, 32 - focal proliferation of epithelial tissues;
- HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35 - malignant neoplasms, such as carcinomas and genital dysplasia.
In addition, with weakened immunity, the human body becomes more susceptible to papillomatous viruses types 26 and 27. In some cases, HPV 30, 34, 37 and 38 can become the cause of benign and malignant tumors.
It is also important to note that some types of papillomatous viruses are transmitted by domestic contact, while others are transmitted sexually.
Types of warts: common, plantar and others, treatment
A very large number of varieties of papillomatous viruses and other causes of the appearance of warts cause different locations of formations and their different characteristics. So, there are:
- Common warts, also called common warts.
They are most often located on the skin of the hands. These growths can vary in color from meat to brown.
- Plantar warts.
These formations grow deep in the tissues, causing painful sensations and accompanied by capillary thrombosis, which bleed even with the slightest damage. Plantar warts require medical treatment, not eliminating them alone or in a beauty salon.
- Flat warts.
Its location, as a rule, is observed in the skin of the neck, face, chest, knee and forearm flexions.
- Anogenital warts, more commonly known as genital warts.
These formations affect the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitals, as well as the perianal region. Its location is possible at the entrance to the urethra with subsequent proximal dissemination.
- Perianal warts.
These formations are most often located in the anus and vagina, as well as in the tissues near the external genitals in women. In men, perianal warts are located in the anus.
- Laryngeal papillomatosis.
This manifestation of the virus occurs mainly in childhood. The masses can be multiple, which represents a special danger to life, causing obstruction of the respiratory tract.
Anogenital warts
Anogenital warts are benign neoplasms located on the skin and mucous membranes of the external genital organs, as well as in the perianal region. All anogenital warts are generally divided into:
- Typical condylomata.
These warts are located, as a rule, at the entrance of the vagina, the anus and also in the inner layer of the foreskin. In their form, these neoplasms may resemble cauliflower.
- Papular warts.
The surface of these neoplasms is smooth and does not contain keratinized layers.
- Hyperkeratotic warts.
Unlike previous warts, the surface of these anogenital formations is covered with particles of keratinized tissue. Most hyperkeratotic condylomas are located on the outer leaf of the foreskin, on the body of the penis and on the scrotum in men, as well as on the labia majora in women.
- Flat warts.
The formations are represented by spots that protrude slightly above the surface of the skin. They are practically invisible and are not always immediately identified by a person.
Giant Buschke Condyloma - Levenshtein
Carninoma-like genital warts occur when the HPV 16 virus enters the body. According to the results of some studies, HPV viruses of types 1, 6, 11, 18, 31, 33, transmitted by contact and sexually, can also cause the appearance of such warts. The second name of such an education is the giant Bushke-Levenshtein condyloma. Its main differences are:
- rapidly progressive increase in size;
- the possibility of re-education after treatment;
- destruction of nearby tissues;
- high probability of malignancy with the subsequent development of squamous cell skin cancer.
Young and old are the most susceptible to this type of cancer. In the male body, the virus manifests itself by the appearance of genital warts in the tissues of the glans and foreskin. Sometimes, the Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma can be located in the integument of the trunk of the penis. In the female body, the formations are usually located in the perianal, anorectal and groin areas. Its appearance on the face, oral mucosa, as well as in other areas of the skin and mucous membranes is not excluded.
Common warts on fingers and other parts of the body
The most common benign skin lesions are common warts, also called common warts. In appearance, these formations are hard and dry eminences on the skin. Its surface is irregular. Sizes vary by a few millimeters. Most of the time, these warts are located on the fingers and hands, as well as on the face. The color of neoplasms is usually greyish, yellowish or skin-colored.
Palmoplantar warts on arms and legs
Warts can easily appear on the palms and soles of the feet. They come in a variety of shapes and colors, ranging from light yellow to dark brown. These epithelial formations are common among the population. They can be superficial and mosaic-like or deep (hyperkeratotic).
The treatment of palmar and plantar warts is complex. A dermatologist, during a complete diagnosis, must necessarily exclude lichen planus and verrucous tuberculosis.
Flat warts on the face

A flat wart is almost always small and has a smooth (rarely scaly) surface. Its color can hardly differ from the color of the skin, as people often live with these formations and do not even notice them. Typically, these flat epithelial formations appear on the skin in whole groups.
The specialist will be able to accurately detect and identify flat warts on the face or, for example, on the back of the hands from the very first consultation. A visual examination will be sufficient for a competent doctor to understand what he is dealing with. If the dermatologist has doubts about the presumptive diagnosis, additional diagnoses, including laboratory tests, can be assigned.
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection
The clinical manifestations of a wart depend mainly on where it was formed. Each individual type of epithelial tumor described above has its own individual characteristics.
- A common wart is characterized by pronounced hyperkeratosis (high rate of cell division in the stratum corneum and flaking).
It may look like a dome-shaped lump or papules. These warts appear mainly in places where the risk of tissue damage is greatest, that is, on the skin of the hands, feet, elbows.
- Flat warts have a flat apex, are small in volume and do not exceed 3-4 mm in diameter.
If a wart is seen in the area of the skin folds, its initial diagnosis can be difficult, because these papules or growths can manifest as flat or common warts.
- Warts on the soles of the feet can be accompanied by a symptom of pain, as these areas of the body are constantly subject to trauma. The center of this epithelial tumor may be slightly depressed.
It is also not uncommon for several warts on the sole to merge into a single structure, forming a specific pattern in the shape of a mosaic.
- With regard to filamentous warts, this problem can appear on the skin of the face.
They grow quickly, so when detected, they try to be removed as a cosmetic defect.
- In addition, warts can be diagnosed in the oral cavity, where the formations are most often represented by small whitish or pink nodules.
This problem is encountered in extremely rare cases, as a rule, at a dental appointment or during a routine examination of the body.
Warts: treatment
Epithelial tumors in the form of warts are treated only under the strict supervision of the responsible physician. Therapy cannot be general, because each individual case of the onset and development of the disease is individual. That is why it is not advisable to use questionable drugs on the advice of friends, advertising or a pharmacist at a pharmacy.
To date, there is no specific therapy for human papillomavirus. That is why the treatment of warts aims to eliminate the symptoms of a viral injury.
If a patient is diagnosed with condyloma, then this type of education necessarily needs a well-chosen therapy, as there is a risk of malignant degeneration.
There are several methods of treating warts, each with its own characteristics. The effectiveness of all therapeutic methods is approximately 70%.
Remedy for warts: external therapy
The treatment of warts is mainly aimed at removing them. It can be done through physical intervention or medication.
With external methods, warts are treated in a complex way. The doctor may prescribe cauterizing drugs and keratolytic drugs. It can be 10% silver nitrate solution, 50% lactic acid solution.
Your doctor may recommend antiviral medications for warts.
Cytotoxic drugs, such as fluorouracil cream, are also topical. Prescribed for the treatment of warts and all types of plasters with salicylic acid (40%).
Physical destruction of warts can be accomplished through liquid nitrogen and electrocoagulation. Chemical destruction of tissues can be carried out with salicylic or trichloroacetic acid, silver and sodium solution, sodium hydroxide.
Immunotherapy is also used. After the wart is removed, your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs.
Removing warts at home is prohibited
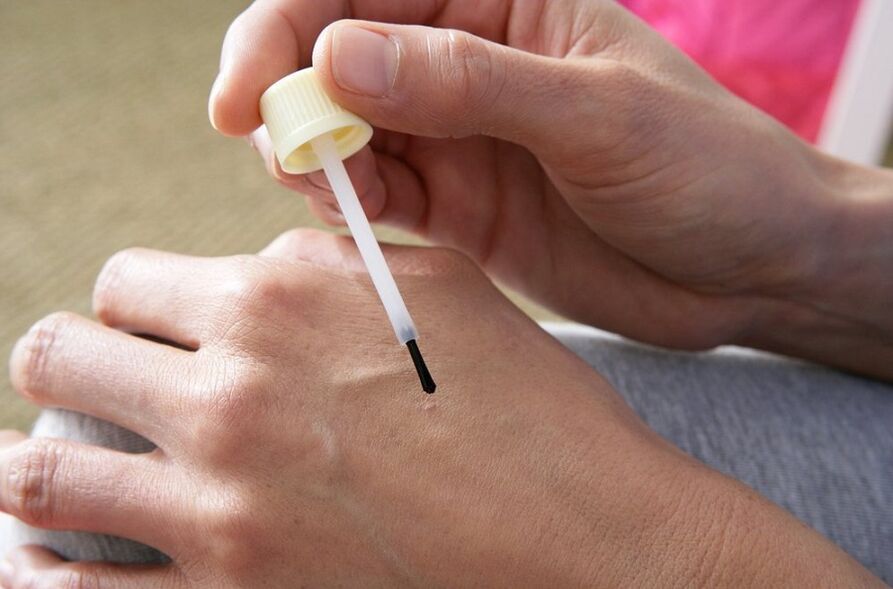
Traditional medicine, according to most, can safely treat many illnesses. But this opinion is erroneous, because decoctions, infusions and all kinds of compresses of essential oils and herbs can play only an auxiliary role and in no case should they be used as the main type of therapy.
In combination with medicinal effects, the assistant specialist can prescribe alternative medicine recipes with celandine, rowan fruit, wormwood, onion, flaxseed oil, milkweed.
Removal of warts at home is not carried out. Education cannot be interrupted with sharp, perforated and cauterized objects. Only a competent doctor, after diagnosing the patient's condition, can prescribe adequate and safe therapy. Be careful and don't rush yourself.
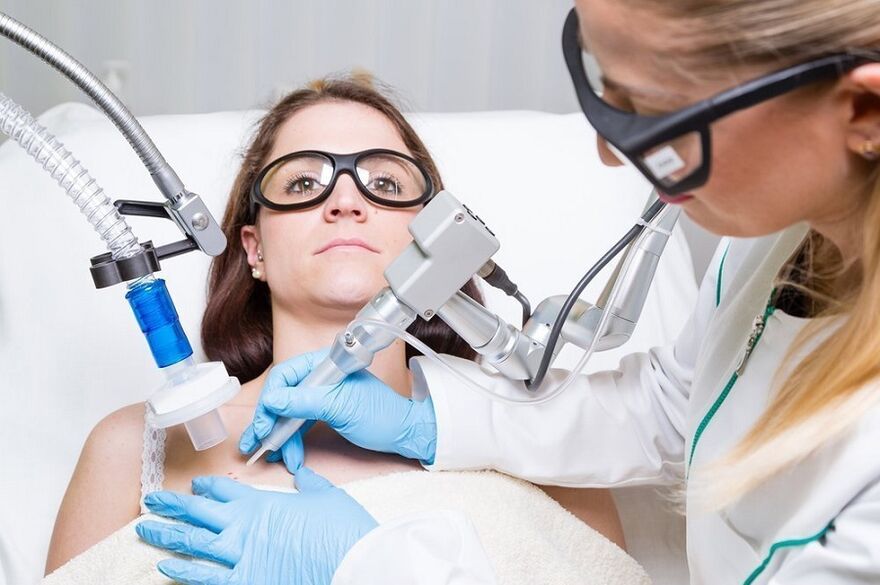
Laser warts removal and other methods
Modern medicine employs several surgical techniques to remove warts.
- Electrocoagulation is one of the most proven methods for removing various warts.
The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia with coagulator. The high frequency current supplied to the steel loop helps to cut the epithelial mass and prevent bleeding during and after surgery.
- Surgical excision is prescribed for extensive skin lesions.
The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia, followed by the imposition of cosmetic sutures, which are removed after about 1 week. A small scar may remain.
- Laser wart removal is the newest method of treatment.
The effect of this manipulation can be in the form of evaporation or coagulation of skin cells. The removal of laser warts is quick and absolutely painless, as the procedure is performed under local anesthesia. After the wart is removed, a small depression may remain, which will disappear after 12-20 days.
Laser removal is now offered by many medical centers and clinics.
- Warts are also removed at low temperatures.
Deep freezing of the tissues leads to their death. This is how the freezing of liquid nitrogen is carried out.
This wart removal is performed using a cryoapplicator or a stick applicator with a cotton swab. In any case, the procedure is effective and takes only a few minutes.
The applicator is applied to the wart (perpendicularly) and lightly pressed on it. The time it takes for an epithelial tumor to freeze depends mainly on its size. It usually takes 7 to 35 seconds to freeze.
It is important to know that any wart removal is not a guarantee that the problem will not reappear. The likelihood of re-formation depends on several factors, including the patient's immune system. According to statistics, a relapse of the disease occurs after 3-4 months in more than 20% of patients. That is why many doctors, along with surgical removal of warts, prescribe general anti-relapse therapy.
Warts prevention

To protect yourself from at least a little bit of a viral infection and reduce the risk of warts on the body, doctors advise you first of all that you have a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary to constantly maintain the immune system with competence, which loses its protective functions due to constant nervous wear, lack of sleep, malnutrition and even lack of vitamins.
Doctors recommend:
- Refuse casual sex. It is advisable to have a permanent and healthy partner.
- Respect the rules of personal hygiene. You shouldn't use someone else's towel, go to a public bath without changing your shoes.
- Treat skin lesions properly.
It is also important to eat well, lead an active lifestyle, get rid of bad habits, get enough sleep, be less nervous, as all of these factors negatively affect the immune system.























